-
PROVIDERS
New MRD Medicare Coverage for Select Indications*
*When coverage criteria are met. Additional criteria and exceptions for coverage may apply.
-
LIFE SCIENCES
Register now
UPCOMING WEBINARTranslating data into an actionable R&D strategy
-
PATIENTS
It's About Time
View the Tempus vision.
- RESOURCES
-
ABOUT US
View Job Postings
We’re looking for people who can change the world.
- INVESTORS
10/14/2025
Impact of Tumor Suppressor Gene (TSG) Alteration (Alt) Burden on Outcomes in Patients (Pts) With Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer (McSpc)
ESMO 2025
PRESENTATION
Authors
D. Kilari, B. Yilma, S. Fragkogianni, U. Jariwala, C. Traverso, J. Mercer, N. Agarwal, E.S. Antonarakis, R.R. McKay
Background – TSG (TP53, RB1, PTEN) alts are linked to poor outcomes in prostate cancer. However, the impact of first-line (1L) treatment (tx) and prognosis based on the TSG alt type and burden (0, 1, ≥2 alts) in mCSPC remains unclear. To inform clinical trial strategies, we investigated the TSG burden and 1L tx outcomes in pts with mCSPC.
Methods – Using Lens Workspace (Tempus AI, Inc., Chicago, IL), de-identified records of mCSPC pts sequenced with the Tempus xT DNA assay were studied (N=2173). Tx consisted of 1L androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) alone or in combination with androgen receptor pathway inhibitors (ARPI) and/or docetaxel. Real-world overall survival (rwOS) was defined from 1L tx start to death from any cause. Median rwOS (mOS) was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and hazard ratios (HR) with Cox proportional hazard models.
Results – In the overall population, median age at diagnosis was 69 yrs, 12% of pts were Black, and 77% had bone metastasis. Compared to the TSG wild type (wt) group, TSG alt mCSPC had lower median PSA levels (80 vs 125 ng/ml, p<0.001) and more visceral disease (19 vs 15%, p=0.01). TSG wt tumors were enriched for CDK12, SPOP, FOXA1, and ATM alts, while TSG alt tumors were enriched for PIK3CA, FAS, and MAP3K1 alts (q<0.01; p<0.05). Among pts with any 1L tx, mOS was inferior in the TSG alt cohort (HR: 1.57; 95% CI 1.32-1.86; p<0.001). The table shows univariate rwOS outcomes based on TSG alt and burden.
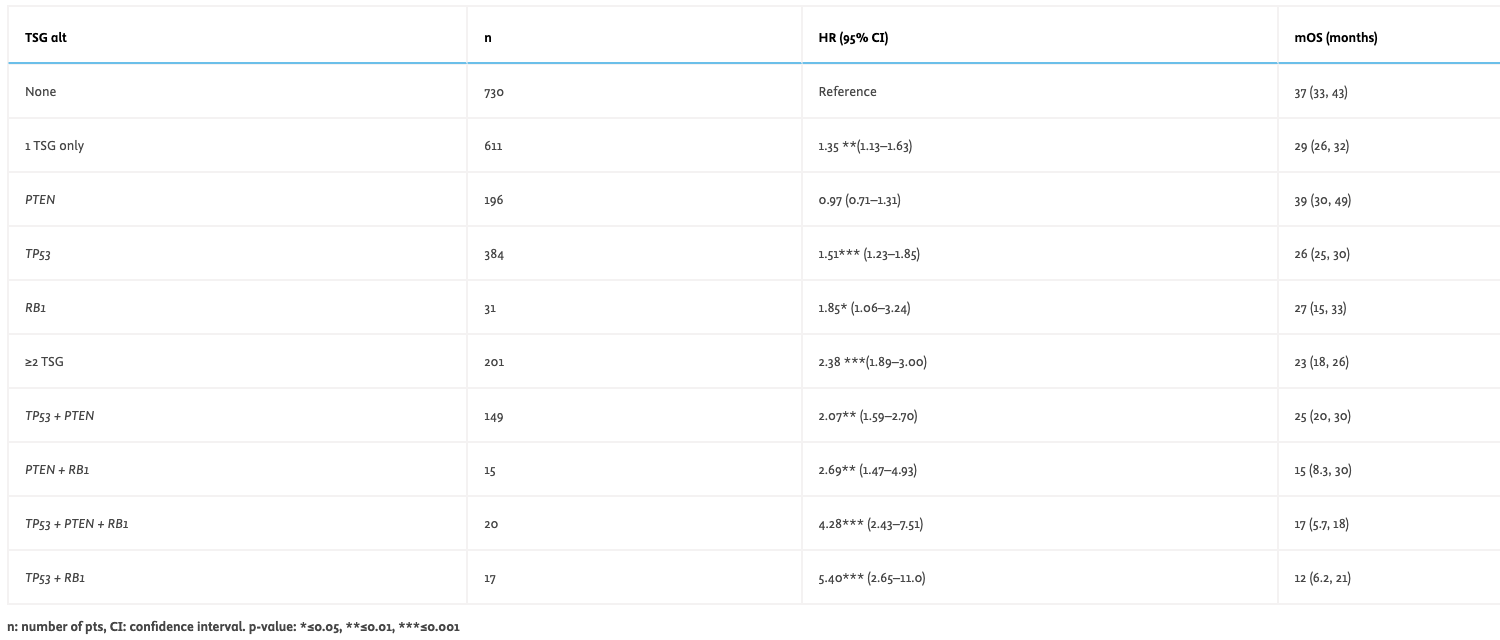
Conclusions – The progressively worse OS post-1L tx in pts with mCSPC and increased TSG burden indicates biomarker-directed intensive tx may be needed for this high-risk group. These findings support the Alliance phase 3 ASPIRE trial that will prospectively evaluate whether adding docetaxel to ADT+ARPI overcomes the poor prognosis conferred by TSG alt.