-
PROVIDERS
New MRD Medicare Coverage for Select Indications*
*When coverage criteria are met. Additional criteria and exceptions for coverage may apply.
-
LIFE SCIENCES
Register now
UPCOMING WEBINARTranslating data into an actionable R&D strategy
-
PATIENTS
It's About Time
View the Tempus vision.
- RESOURCES
-
ABOUT US
View Job Postings
We’re looking for people who can change the world.
- INVESTORS
01/05/2026
Use of Transcriptomic Signatures of RAD51 and GATA6 Predict Improved Real-World Overall Survival with Platinum Therapy in BRCA/PALB2 Wild-Type Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer
ASCO GI 2026
PRESENTATION
Authors
Binbin Zheng-Lin, Ellen B. Jaeger, Cody Eslinger, Stamatina Fragkogianni, Unnati Jariwala, Arya Ashok, Kayla Viets Layng, Taro Shibuki, Oluseyi Abidoye, Celine Hoyek, Angelo Pirozzi, Daniel H. Ahn, Jeremy Clifton Jones, Christina Wu, Mitesh J. Borad, Mohamad Bassam Sonbol, John H. Strickler, Takayuki Yoshino, Masafumi Ikeda, Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab
Background: DNA-damaging agents improve outcomes in metastatic pancreatic cancer (mPC) with homologous recombination repair (HRR) deficiency, albeit use is limited to 6-9% of patients (pts) with BRCA1/2 or PALB2 mutations. We hypothesized that BRCA/PALB2 wildtype mPC may exhibit platinum sensitivity driven by altered HRR gene expression. We correlated HRR gene RNA profiles with real-world overall survival (rwOS) following first-line (1L) platinum therapy (PT).
Methods: Tempus Lens, a platform used to query multimodal data from millions of de-identified patient records in the Tempus Database was used to identify mPC pts with wildtype somatic BRCA1/2 and PALB2 who had Tempus xT DNA and xR RNA testing. RNA-seq data were normalized to correct for assay/batch effects, quantified as transcripts per million (TPM) and reported as log2(TPM+1) for 17 HRR genes and GATA6. Pts were classified as high and low expressors based on the top and bottom quartile gene expression. Pts were grouped as PT-treated (received 1L PT) or PT-naïve (never received PT). Real world overall survival (rwOS) was calculated from 1L start to death or loss to follow up. Risk set adjustment was applied to mitigate immortal time bias. Median rwOS was estimated using Kaplan-Meier and univariate Cox models. A multivariate Cox Proportional (CoxPh) model included PT use, RAS status, and expression of genes (as continuous variables).
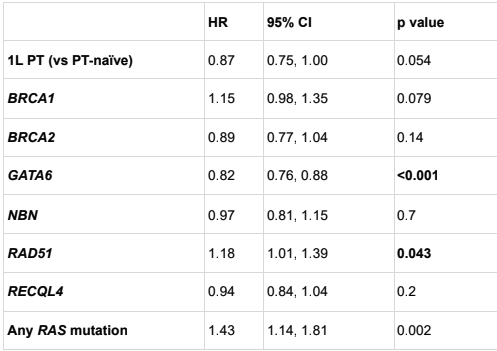
Results: Among 1,068 pts, the median age was 66 years and 609 (57%) received 1L PT. In low RAD51 expressors, PT-treated pts (n = 136) had significantly longer rwOS than PT-naïve (n = 112): 11.4 months (95% CI, 7.8–13.8) vs 8 months (95% CI, 5.5–9.0); p = 0.028. In contrast, in high RAD51 expressors, rwOS was similar between PT-treated (n = 150) and PT-naïve (n = 97): 7.9 vs 6.9 months (p = 0.236). High GATA6 expression was also associated with improved rwOS in PT-treated pts vs PT-naïve: 13.5 vs. 9.3 months; p = 0.011. In multivariate analysis, increased GATA6 expression remained a positive predictor of rwOS (HR 0.82; 95% CI, 0.76–0.88; p < 0.001), and high RAD51 expression was associated with shorter rwOS with PT (HR 1.18; 95% CI, 1.01–1.39; p = 0.043).
Conclusions: In BRCA/PALB2wt mPC, transcriptomic profiling identified low RAD51 and high GATA6 expression as predictors for improved rwOS when treated with PT. Integrating these biomarkers may improve development of DNA-damaging therapies beyond canonically defined HRD.
Table 1: Hazard ratios of mPC mortality by selected HRR genes estimated by multivariate CoxPh models.